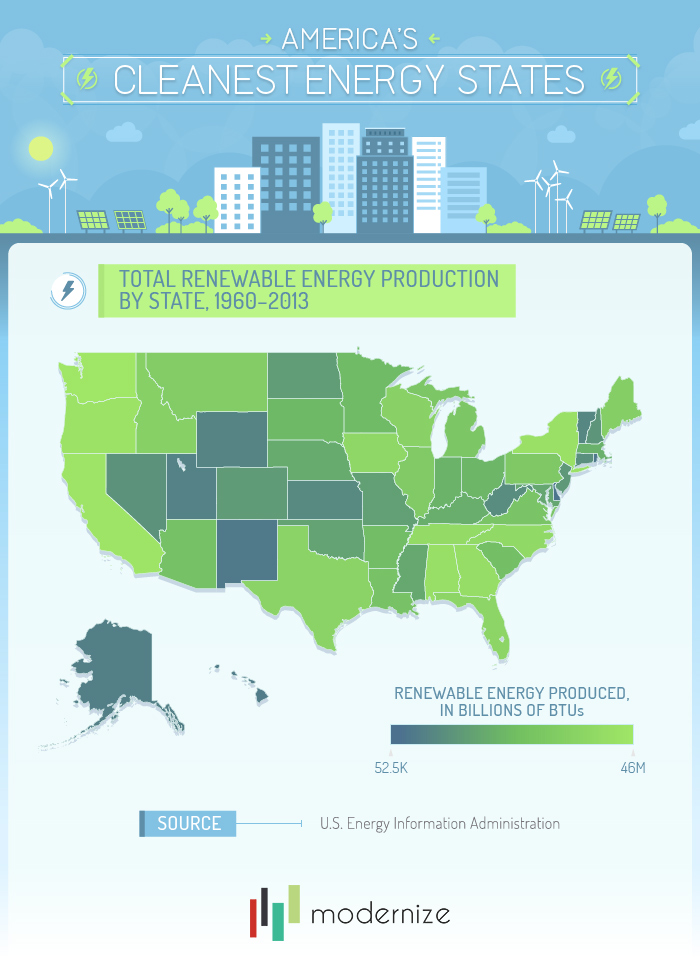
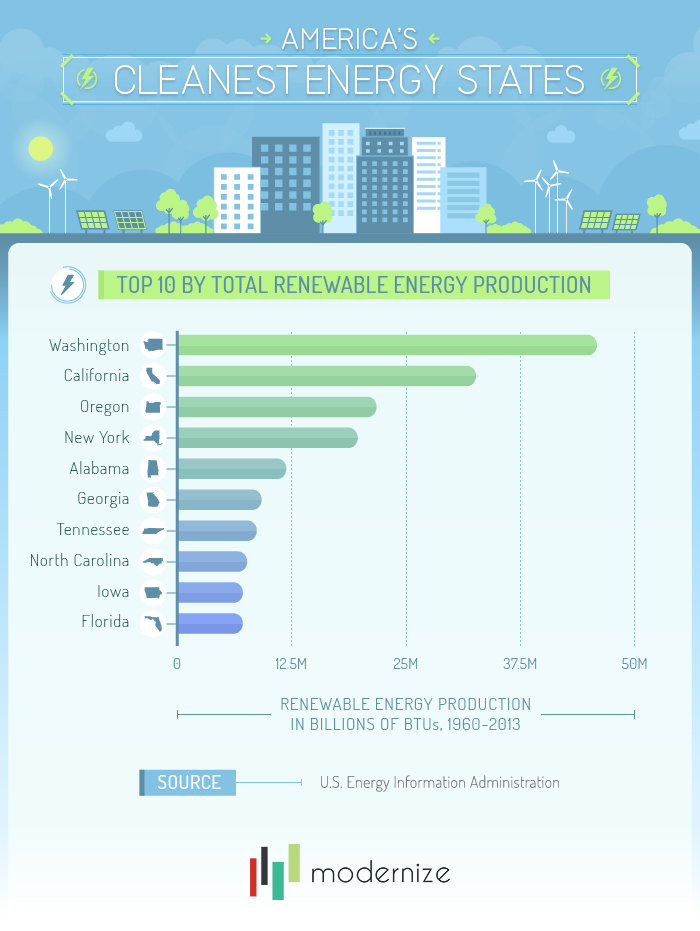
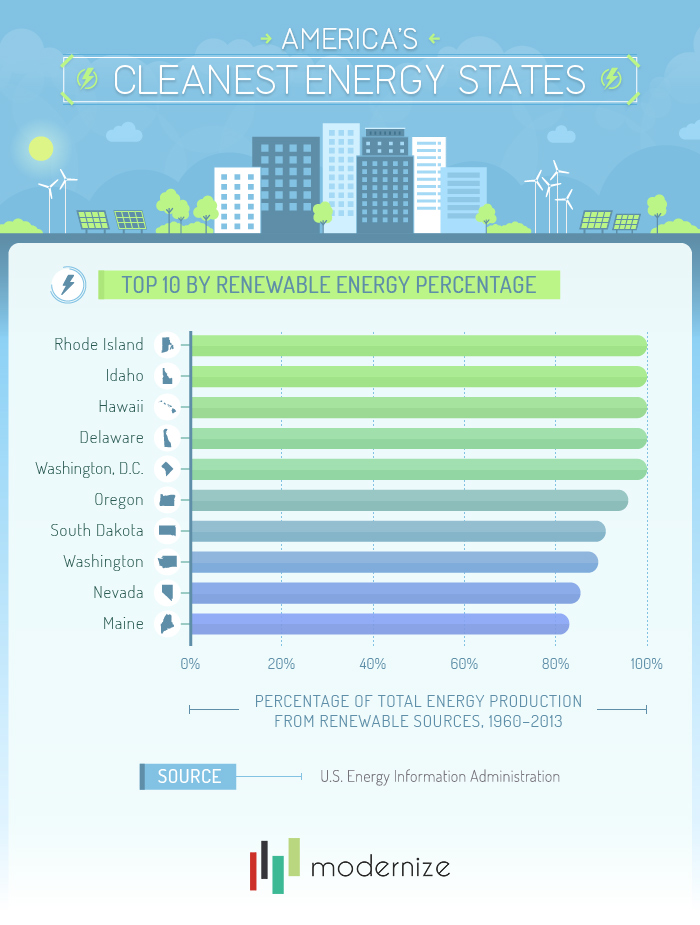
Seeing USA’s Terrain from the Plane
As I was flying across the USA to visit family in Colorado I noticed so many changes to the terrain. As we took off from New Jersey I saw suburban areas with lots of green grass, trees and of course swimming pools. Then after about 45 minutes some farmland as well as small towns and a few large cities. But, I want to discuss the differences I noticed out my window since the last time I flew across the country.
Rivers and Streams
We were in the air about 1 hour and I noticed a lot of changes. Some of the rivers below had dried up. All you could see was sand-colored curvy dirt and grass where the water should be.
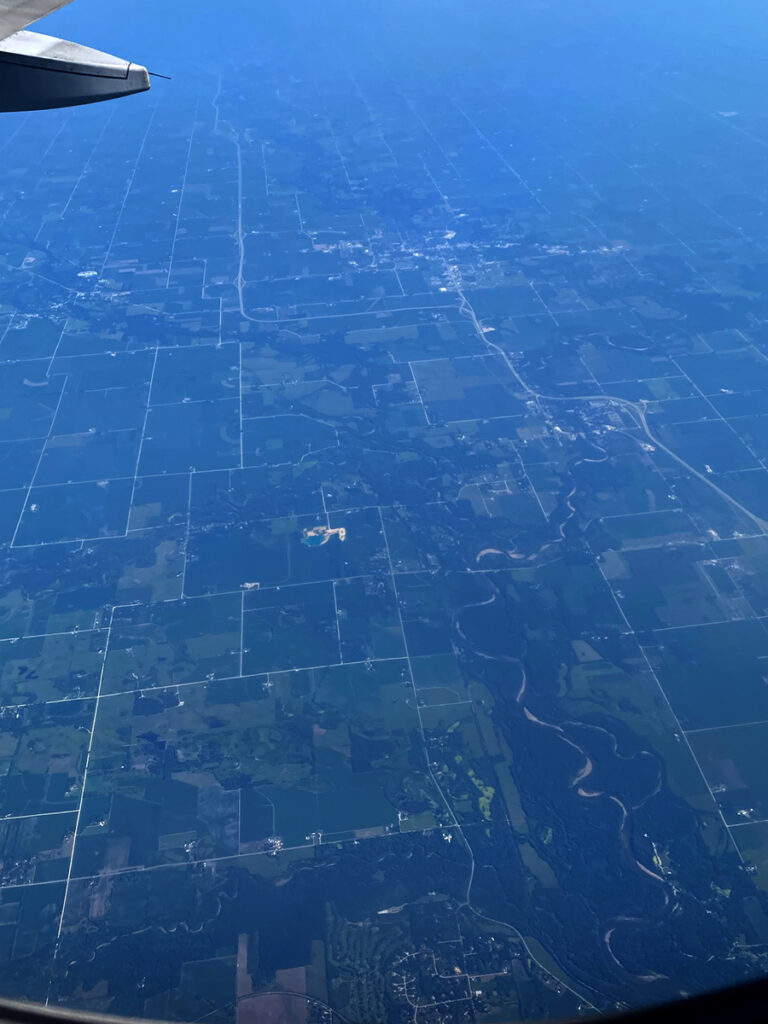

The west is in a drought but seeing the rivers closer to the east coast empty of precious water was sad. Also, we weren’t yet in the west, so the drought is definitely spreading across the country.
From the USGS website:
“Water in the western United States is disappearing, and several states are facing severe water shortages as drought conditions worsen. Many streams are drying up, and there is growing concern that this trend will only continue as climate change produces warmer and drier conditions. The loss of stream ecosystems has far reaching ecological, social, and economic implications. Species that depend on these ecosystems for habitat will be at greater risk of extinction and humans will lose vital sources of water relied upon for agriculture, drinking water, and recreation.”
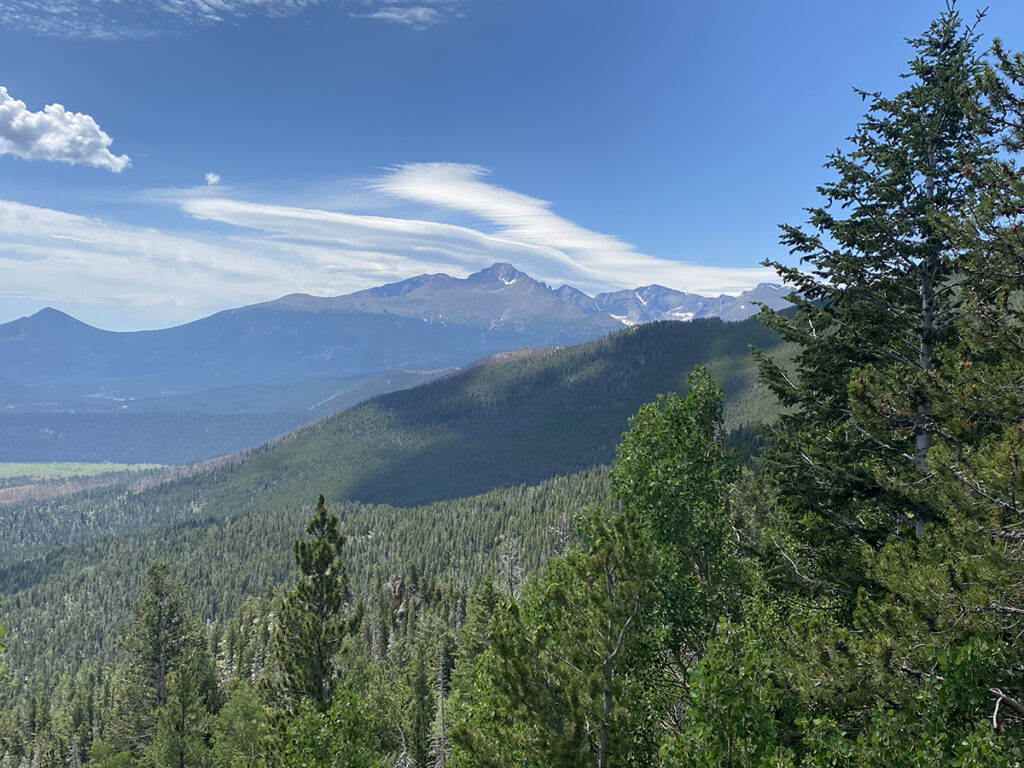
Once on the ground in Denver and driving into the Rocky Mountains I’m happy to report the area was very green and lush. Much more so than the last time I had visited. Back in 2018 the area was being devastated by the mountain pine beetle and there were so many brown trees and the landscape was so dry.

Wind Turbines
I’ve flown across the country many times but this was the first time I’d seen so many wind turbines on farms and ranches. Yes, the idea that rural America is harvesting wind energy got me excited. The ground below is always so cool from a plane because of all the crop circles. This time though I was seeing circles and squares and in the corners were wind turbines. Hundreds of them. It seems like so many but actually they look very small in comparison to the land.
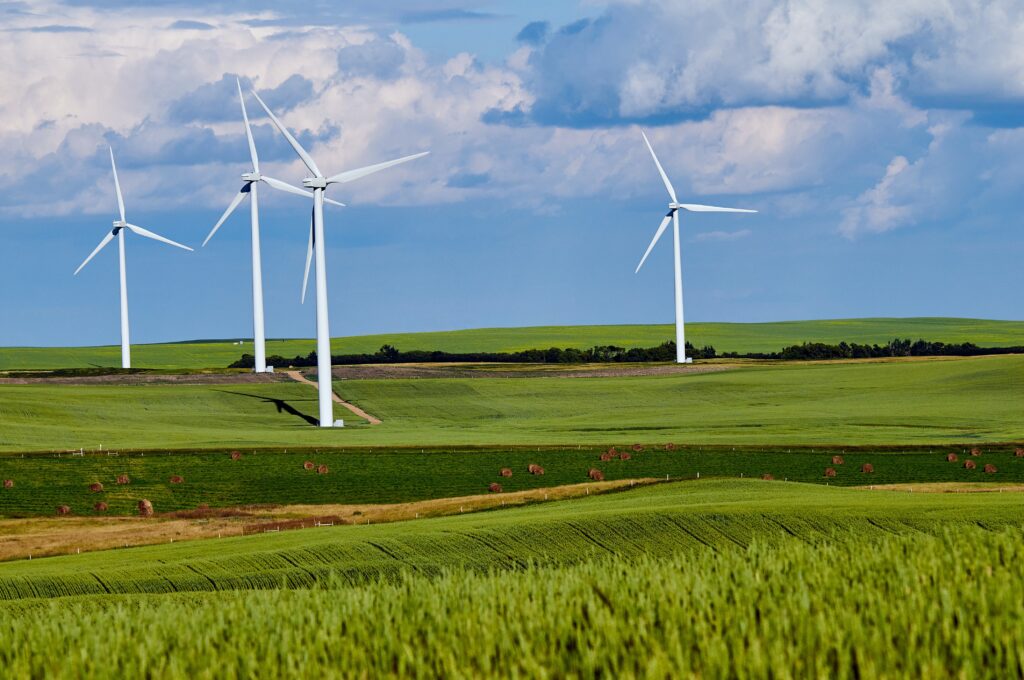

From: Focus on Agriculture
“Each turbine uses less than half an acre, so farmers can plant crops and graze livestock right to the turbine’s base…
…Wind energy also has no emissions and preserves water compared with other power generation methods, saving some 87 billion gallons in 2016 alone.”
So, wind turbines can help us conserve water. Are there plans to build them in the east? YES!
As of July 5, 2023:
The U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management on Wednesday approved the construction of up to 98 wind turbine generators off the coast of Atlantic City, N.J., as part of a Biden administration plan to install offshore wind sites along the country’s coasts.
This all sounds great except with one advancement comes another step back. If they are building wind turbines along the coast from Cape Cod to North Carolina, what can we do about migrating birds?
They will need to navigate away from the turbines and certain flocks may have a hard time given how many are being built. But, the power of the wind and the advantages to impacting global warming some will say outweigh the harm to birds.