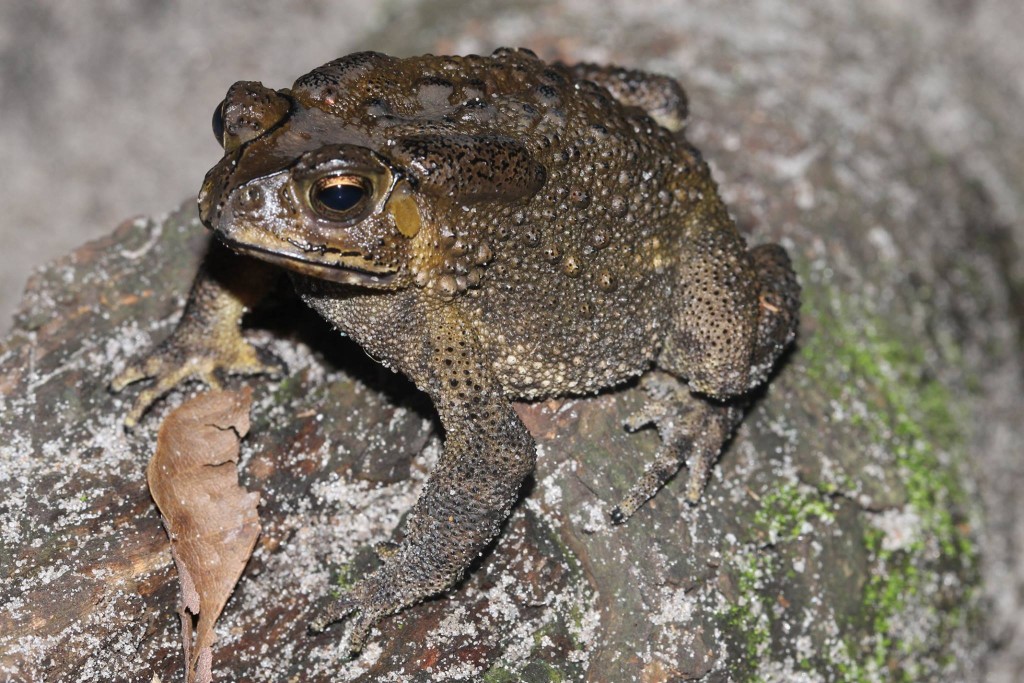
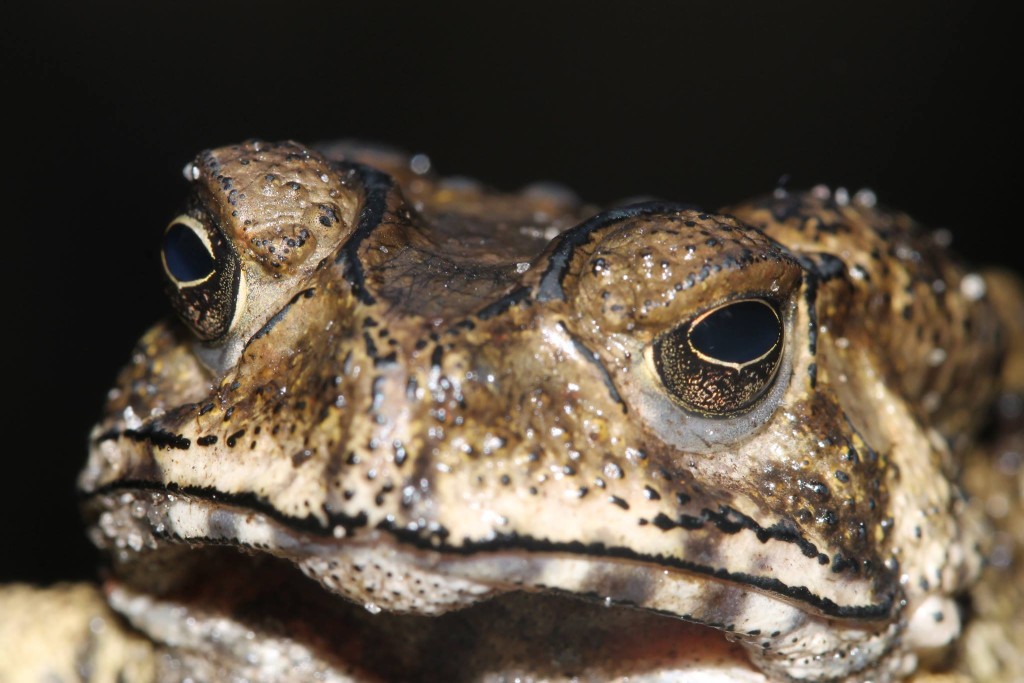
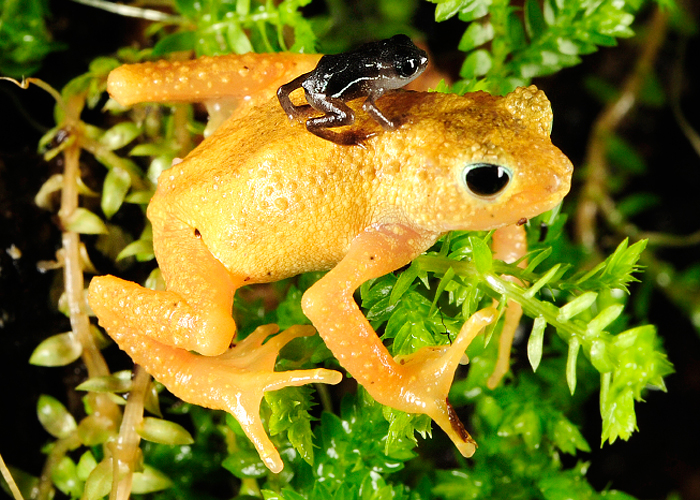
Recently I’ve been meeting children at my Frogs Are Green table at various Jersey City events and this one young girl told me she had at home: fire-bellied toads, a lizard, fish, 2 dogs and her brother had turtles too.
Growing up my parents weren’t so keen on animals in the home and perhaps that’s why I love wildlife so much, watch nature programs, and have my own pets. Over the years I’ve had fish, turtles, and cats.

It got me thinking about all that variety from someone so young, and whether it’s a good idea for a child to be responsible for so many pets. In addition, I was quite surprised to hear she had frogs. At first I thought she was joking with me. But a few days later, I heard from another young boy that he also had fire-bellied-toads at home.
It’s not something I recommend because there are so many issues right now with frogs potentially carrying the chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) disease and if those frogs were let go or escaped into an area unnatural to them, they would be helping spread the disease.
(To learn more about this, Save The Frogs has a great web page on this:
Chytrid Fungus in the Pet Trade
“As the trade of amphibians is highly unregulated, disease testing of amphibians traveling between countries and states is next to none. Many amphibians that travel often are carries of the chytrid fungus, which is greatly responsible for the amphibian declines around the world. Approximately 300 species have been detected with chytrid and it is now present in nearly 40 countries. In 2011, a study found that in many pet shops and pet expos nearly 3% of the captive amphibians tested positive for the presence of chytrid, and 13.6% of the collections yielded at least one positive result.” — from Save the Frogs
Frogs As Pets
I decided to look further into how common it is for kids to have pet frogs and found this informational web page: “Your First Frog.”
It’s obvious from reading this page how complex taking care of a pet frog would be. Once you finish this page, I’m sure you’ll agree they belong in the wild.
Only those that are threatened with extinction and are being helped by scientists/herpetologists in captivity like the Golden Mantella, or those doing important research to help amphibians, should have them away from their natural habitats.
___________________________________________________________________
Here are some thoughts on this topic from David Veljacic, nature and wildlife conservationist…
When deciding to buy a child a pet there some questions to keep in mind.
Is my child responsible enough to care for a pet? Never buy children pets to teach them responsibility.
Is this interest a fad?
What is my child looking for in a pet? Does Your child want a playmate or a piece of nature?
Do I have the space?
Does my child have the time? With kids enrolled in so many activities they simply may not have the time to care for the animal properly. Ultimately, the parents have the responsibility to pick up the slack that the kids may leave.
Can we afford the upkeep?
And, if looking at exotics – Is it captive bred? Only buy captive bred animals.
Once You have decided to let Your child have a pet, You need to educate Yourself on the needs of the animal You are buying. You may be called upon to care for the animal from time to time. It is also good, particularly with young kids, to check up on the pets to make sure things are going well, so You should know a little about it.
I have seen it happen many times with people who keep exotics, particularly reptiles and amphibians, where it becomes an obsession to buy more and more species. There is always a new color morph or new species available, and it can be very tempting. I recommend not growing a collection too quickly, a child can become overwhelmed before they know it.
Do Your research! NEVER include pet store workers opinions in Your research! Pet store workers are there to sell You things, then sell You more things. You need have the type of animal You plan on buying researched before heading to the pet store, or breeder, and the only questions left should be things like…
Is the animal captive bred?
Is the animal eating/pooping properly?
You should also be allowed to inspect the animal for obvious injuries.
Many exotics that in the past were sold as “disposable” live for years, even decades. If You cannot commit to a long lived animal, don’t buy one. Never release captive animals into the wild.

 Guest post by Leigh-Ann Brady, who resides in NJ with her 8 year son. She is an artist and writer who is also concerned about the environment.
Guest post by Leigh-Ann Brady, who resides in NJ with her 8 year son. She is an artist and writer who is also concerned about the environment.




